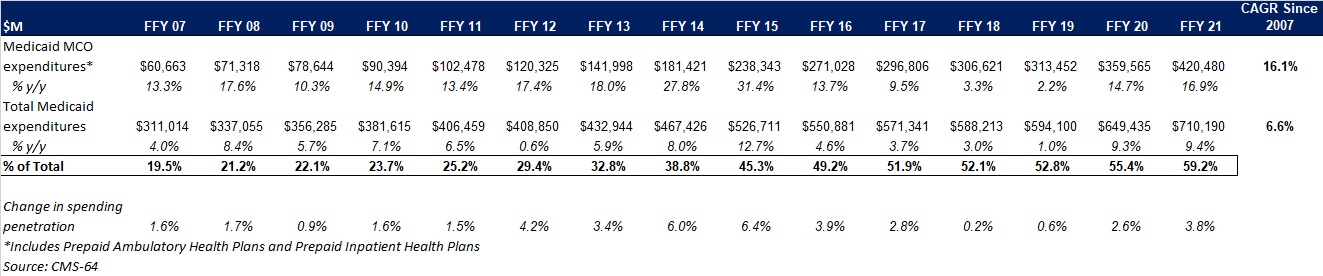
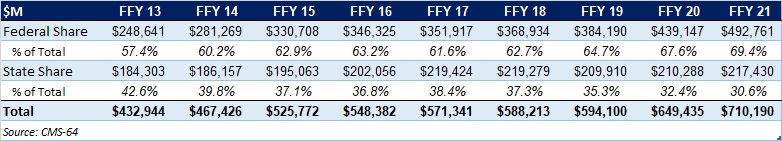
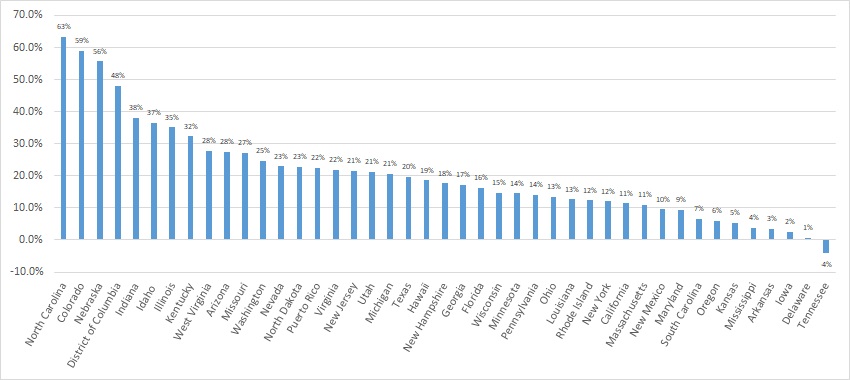
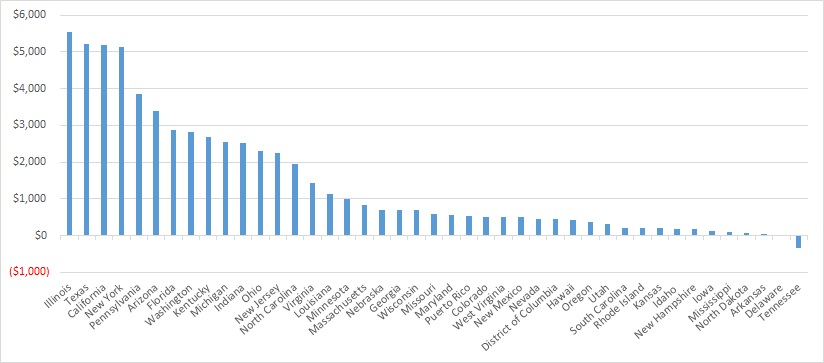
This week, our In Focus section looks at the current federal policy landscape and trends and the legislative outlook for the remainder of 2022 and beyond. Experts from HMA continue to monitor developments in this area and provide additional updates as more information becomes available.
Legislative Branch
To date in 2022, Congress passed multiple comprehensive bills, including the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), which was signed by President Biden on August 16, 2022. The IRA extends Exchange plan premium tax subsidies through 2025, institutes an out-of-pocket drug spending cap for Medicare beneficiaries, expands Medicare, Medicaid, and CHIP coverage protections for certain vaccines, allows Medicare to negotiate drug prices, and implements a penalty payment in the Medicare program for prescription drug prices that rise faster than the rate of inflation.
Going forward, stakeholders have an extensive list of immediate Medicare payment issues for Congress to tackle while lawmakers continue to consider fundamental reforms to the program. Priorities include mitigating Medicare payment reductions scheduled for 2023; providing relief to address inflationary cost pressures; extending the 5 percent bonus for physicians participating in Advanced Alternative Payment Models (APMs), which expires at the end of 2022 for Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs); and permanently expanding telehealth access and payment policies after the federal COVID-19 public health emergency (PHE) declaration expires. Many stakeholder groups are also urging the Senate to act on the House-approved legislation, Improving Seniors Timely Access to Care Act (H.R. 3173), to reform Medicare Advantage prior authorization policies.
Congress did not include major Medicaid proposals in the Inflation Reduction Act. Medicaid stakeholders want Congress to revisit certain Medicaid policies in one of the remaining legislative vehicles this year. Significant proposals of interest include closing the Medicaid coverage gap in non-expansion states, enhanced coverage for justice involved populations, and expanding support for home and community-based services (HCBS). States and some stakeholders have also sought more certainty in the timing and guardrails for ending the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency (PHE) policy that links enhanced federal Medicaid funding with the requirement for continuous Medicaid coverage.
Congressional leaders and key influencers are laying the groundwork for 2023 legislative efforts. Congress is likely to defer action on most major legislative issues until after the November mid-terms, including finalizing federal fiscal year 2023 funding for most departments. A change in control of either or both chambers of Congress will likely lead to greater scrutiny of the Biden Administration’s health care policies and actions, which have largely gone untested by this Congress.
Executive Branch
Executive orders have been a major source in driving federal workstreams in 2022. Following enactment of several major bills, implementation responsibilities have shifted to the Executive Branch and stakeholders will have multiple opportunities to further shape and support new programs, regulatory and policy updates, and funding opportunities. Executive orders passed include:
- Advancing Racial Equity and Support for Underserved Communities, January 21, 2021
- Promoting Competition in the American Economy, July 9, 2021
- Improving the Customer Experience, December 13, 2021
- Access to Affordable, Quality Health Coverage, April 5, 2022
- Equality for LGBTQI Individuals, June 15, 2022
- Protecting Access to Reproductive Healthcare Services, July 8, 2022
The Administration will continue to address COVID-19 emergency needs while stepping up efforts to support states, health plans, providers and other stakeholders as they prepare for the post-COVID environment. The current PHE declaration expires October 13, 2022, but since HHS has not signaled that it plans to end the PHE in October, another extension is likely until January 11, 2023. The next advance notification about the end of the PHE would be Nov. 12, 2022. Once the PHE declaration expires, numerous Medicare and Medicaid, TANF, and SNAP flexibilities will end, including Medicaid’s continuous coverage requirement and certain telehealth flexibilities, among others. Additional federal agency guidance is expected to support post-PHE transitions.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) plans to advance new policy direction across several service and delivery areas, including strengthening long-term services and support and innovations via Section 1115 demonstration programs. CMS is expected to approve transformational 1115 proposals in additional states. Several state proposals focus, in part, on building capacity among local and regional entities and community-based organizations to address social drivers of health. Many state proposals are also strengthening behavioral health delivery systems and seek to meet enrollees’ urgent behavioral health needs. Additionally will want to monitor CMS’ regulatory efforts to align and strengthen managed care and fee-for-service (FFS) access and network adequacy policies as well as updates to the agency’s in lieu of services policy in managed care programs.
The Administration is also expected to accelerate work on its top policy priorities and regulatory agenda in advance of the next Presidential election, and this will require ongoing engagement among health care stakeholders.
For additional information on these and other policies, please contact Andrea Maresca, Amy Bassano, Zach Gaumer, Jon Kromm, or Kevin Kirby.