This week's roundup:
- In Focus: Medicaid Managed Care Profitability: Navigating Margin Pressures and Regulatory Shifts in 2024

- HMA Conference: Strategies and Reforms Shaping Medicare’s Future

- Former Senior FDA Leader Julie Tierney Joins Leavitt Partners

- Arizona Joins Multi-State ArrayRx Consortium to Lower Prescription Drug Costs

- Colorado HCPF Director Pledges to Mitigate Medicaid Cuts, Limit Coverage Loss Under H.R.1

- Indiana Projects Medicaid Cost Surge, Adopts Cost-Saving Actions

- Minnesota Releases Medicaid Provisions, Impacts from H.R. 1

- North Carolina Stopgap Budget Leaves Medicaid $319M Short, Cuts Loom

- Oregon Delays Medicaid Reentry Program Due to H.R.1

- MACPAC Releases Issue Brief on Medicaid Financing

- Ten Million Could Lose Coverage Under H.R.1 by 2034, CBO Forecasts

In Focus
Medicaid Managed Care Profitability: Navigating Margin Pressures and Regulatory Shifts in 2024
This week, our In Focus section highlights findings from Health Management Associates Information Services’ (HMAIS’s) review of 2024 statutory filings submitted to the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC). These filings provide a nationwide view of Medicaid managed care plan profitability and medical loss ratios (MLRs) across 221 plans operating in 39 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico.
These data build upon and offer additional context to a previous analysis conducted by HMA and Wakely, an HMA Company, of increasing post-pandemic financial pressures driven by acuity increases resulting from the continuous eligibility unwinding and increases in behavioral health and home and community-based services access and utilization.
Medicaid Managed Care Underwriting Gains and Losses
As state Medicaid programs have increasingly moved from fee-for-service to managed care, a foundational assumption has been that efficient managed care organizations (MCOs) reduce waste and deliver high quality, cost-effective healthcare services. This transition has made Medicaid plan performance and sustainability a central focus for policymakers and actuaries alike.
Medicaid capitation rates must be actuarially sound, which means they must be projected to cover all “reasonable, appropriate, and attainable costs,” including medical administrative costs, plus a margin for insurance risk, even for nonprofit plans. According to the Society of Actuaries 2024 research, average underwriting margins in Medicaid rates ranged from 0.35 percent to 3.15 percent, with a consistent average between 1.2 percent and 1.3 percent.
However, actual results often deviate from projections for reasons that may be challenging to predict. Rate setting is an inherently forward-looking process, and even with conservative assumptions, unexpected shifts in enrollment, acuity, or service utilization can lead to significant deviations from projected results. Retrospective reviews show variability in margins over time (see Figure 1).
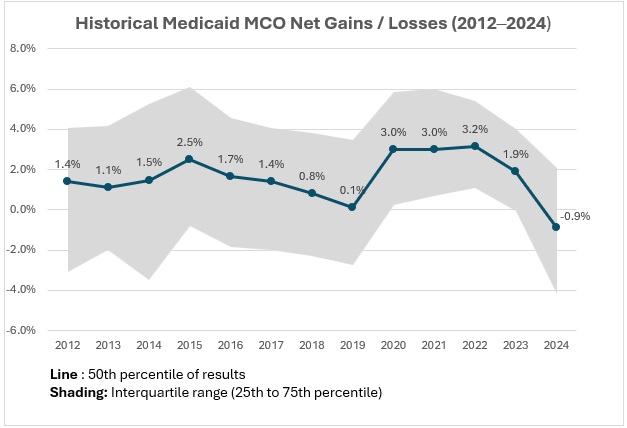
Figure 1. Historical Medicaid MCO Net Gains/Losses, 2012‒2024 (39 States, DC)
Based on HMAIS’s analysis, Medicaid MCOs sustained modest but steady gains from 2012 through 2017. After a decline between 2016 and 2019, margins rebounded to approximately 3 percent until 2022, narrowed in 2023 to 1.9 percent, and turned negative in 2024 at -0.9 percent.
For the first time in over a decade, more plans experienced losses than gains in 2024 (see Figure 2), with only 42 percent reporting positive margins, down from the decade high of 84 percent in 2022. This shift raises critical questions about sustainability and participation in Medicaid managed care.
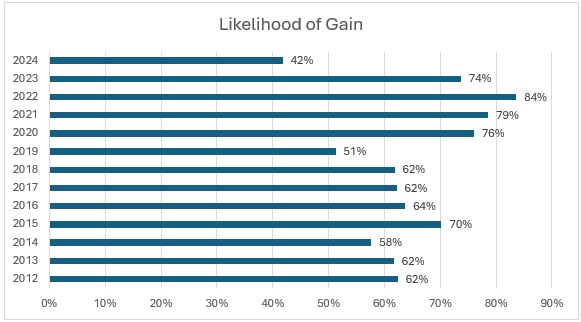
Figure 2. Medicaid Managed Plans Likelihood of Gain, 2012‒2024 (39 States, DC)
The “Likelihood of Gain” chart tracks the percentage of Medicaid managed care plans reporting an underwriting gain each year from 2012 to 2024. For most years, the likelihood that a plan posted a gain was relatively high, typically between 60 percent and 80 percent. The probability reached a recent peak in 2022, with 84 percent of plans reporting gains, and remained elevated in 2023 (74 percent). In 2024, however, the likelihood of gain dropped sharply to just 42 percent, the lowest level in the 12-year period.
Risk Corridors, Medical Loss Ratios, and Structural Policy Shifts
MLRs show the portion of plan revenue spent on medical care as compared with the costs to operate the plan and the underwriting gain or loss described previously. When MLRs rise or fall, it can be an indication that medical cost trends experienced by health plans differ from the assumptions used by state rate setting actuaries. High MLRs are the key driver of underwriting gains, and low MLRs are associated with higher profitability. All states report MLRs to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), and some enforce minimum MLRs with a remittance provision, requiring plans to return funds if their MLR goes below a certain level.
Risk corridors are another tool that states use to manage financial volatility. These mechanisms share gains or losses between plans and states when results deviate significantly from pricing assumptions, offering protection to MCOs and the state alike, in contrast to minimum MLR provisions with a remittance provision, which only protects the state. During the COVID-19 pandemic, many states implemented or expanded risk corridors to recoup overpayments because of lower utilization. Some risk corridors were set retroactively—a practice CMS now prohibits.
In 2024, MLRs reached a decade high of 90.8 percent, as indicated by HMAIS’s analysis. Driving this increase were heightened utilization rates, increased enrollee acuity, and the end of continuous Medicaid coverage protections in 2023. As healthier, lower-cost members left Medicaid, plans were left serving a more complex population with higher per-member costs. Inflation in medical costs—especially for behavioral health and home and community-based services—added more pressure. Delayed or avoided care during the COVID-19 pandemic may also have played a role, as members sought more services in 2022‒2024, resulting in a surge in utilization greater than what was priced into rates.
Many states put risk corridors in place to stabilize margins from 2020 to 2022, which may have contributed to the tight band of outcomes around the high underwriting gains in that period. However, many states have been removing them for 2024, 2025, and 2026. Without these protections, plans may face greater exposure to underpayment in 2025 and 2026 if cost trends continue to outpace rate assumptions.
What to Watch
Rate setting conversations between states and plans for 2026 are happening now, and in many cases they are quite challenging. In addition to meeting actuarial soundness requirements, states also must balance their budgets, and some may be facing limitations on their traditionally used tools.
Looking ahead, it will be increasingly important that states and plans partner to find cost savings that can ensure the program’s long-term sustainability.
A subscription to HMAIS provides access to comprehensive financial intelligence on Medicaid managed care. Far beyond surface-level snapshots, HMAIS delivers health plan-level financial performance metrics, enrollment trends, and state policy developments that directly shape rate setting and operational strategy. Whether you’re a state official, health plan executive, or policy strategist, HMAIS provides the financial clarity and policy context needed to anticipate regulatory shifts, benchmark performance, and make confident, data-driven decisions.
For questions about the analysis discussed in this article, contact Gabby Palmieri at [email protected].
Strategies and Reforms Shaping Medicare’s Future
As Medicare enters a new phase of transformation, the Health Management Associates (HMA) 2025 National Conference in New Orleans, LA, offers a timely and essential forum for healthcare leaders to explore the policy and operational shifts that are shaping the future of the program. On October 14‒16, 2025, attendees will have access to a robust lineup of sessions designed to unpack the implications of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS) evolving strategy and provide actionable insights for payers, providers, and investors.
Reimagining Value-Based Care: A Main Stage Conversation
The conference’s main stage session, Shifting the Paradigm: Transforming Value-Based Healthcare for Lasting Impact, will explore how CMS is redefining expectations around global risk, consumer engagement, and return on investment. This conversation will spotlight the intersection of policy and practice, with speakers who bring deep expertise and diverse perspectives, including:
- Liz Fowler, Senior Advisor, HMA, and former Deputy Administrator and Director, Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation, CMS
- Kate Goodrich, MD, MHS, Chief Medical Officer, Humana
- Chris Klomp, Deputy Administrator and Director, Center for Medicare, CMS
Together, they will examine how value-based care is evolving across Medicare Advantage and chronic disease prevention and what it means for care delivery and system sustainability.
Workshops that Deliver Operational Clarity
Two expert-led workshops will take a deeper dive into the policies and mechanics of the changing Medicare landscape.
During the workshop, Medicare Models, Markets, and Momentum: What They Mean for Payers, Providers, and Investors participants will explore the most consequential changes in Medicare Advantage, including expanded risk adjustment validation (RADV) audits, coding accuracy expectations, and the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in compliance and care design.
Speakers include:
- Carrie Graham, PhD, Research Professor and Director, Medicare Policy Initiative, Georgetown University Center for Health Insurance Reform
- Dan Jones, Senior Vice President, Alliance of Community Health Plans
- Neil Patel, MD, Chief Health Officer, Patina Health
The conversation will continue with a workshop focused on Medicare’s shift toward prevention, person-centered care, and accountable innovation, which are intensifying the financial stakes for Medicare providers, organizations, and beneficiaries. During the session Delivering on the Promise of Payment Reform: Operational Strategies for Success speakers will explore how these priorities are shaping real-world models—especially for chronic conditions—and what they mean for payers, providers, and investors. They will unpack the growing use of downside risk, capitation, and upfront investments, and make the case for why payers and providers should invest in these models—and how to evaluate return on investment through both cost savings and improved outcomes. Speakers will include Julius Bruch, MD, PhD, Isaac Health.
Why These Sessions Matter
Medicare’s transformation is not just a policy shift—it’s a strategic imperative. These sessions offer clarity on CMS’s latest agenda, practical guidance from seasoned experts, and real-world strategies that attendees can bring back to their teams. Whether you’re navigating payment reform, operational redesign, or investment strategy, the Medicare track at HMA’s 2025 National Conference is designed to meet the moment.
Explore the full agenda and register.
Former Senior FDA Leader Julie Tierney Joins Leavitt Partners
Leavitt Partners, an HMA Company, is pleased to announce that Julie Tierney has joined the company’s team of health policy experts as a principal, located in Washington, D.C.
Tierney is a proven executive with more than 20 years of FDA legal, policy, and operational experience. She held a number of senior roles at FDA, including FDA chief of staff, overseeing more than 19,000 staff and a budget of more than $7 billion, and most recently served as deputy of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. She is an attorney with professional experience working in the FDA Chief Counsel’s office, on Capitol Hill and private legal practice.
During her career, Tierney has advanced novel policy solutions for regulatory challenges associated with cutting edge technologies, such as overseeing the development of new regulatory pathways for cell and tissue-based products and for genome editing products using a platform approach. She coordinated FDA responses to multiple public health crises and led several initiatives to help accelerate the development of therapies for patients with rare diseases, including the launch of the FDA Rare Disease Innovation Hub.
At Leavitt Partners, Tierney will help life sciences companies, patient organizations, and others understand and develop regulatory strategies and advance policy solutions for complex issues throughout the product life cycle. Her focus on FDA regulatory strategy and policy builds on a decade of Leavitt Partners’ work helping clients drive FDA policy solutions to put safe and effective medicines into the hands of patients.
“We are excited to have Julie bring her deep expertise in food and drug law and policy, FDA agency experience, and strong stakeholder relationships to our team,” said Josh Trent, chief executive officer of Leavitt Partners. “While we live in an era of increasingly personalized medicine and medical breakthroughs, the life sciences sector is facing a wide range of nuanced and interconnected policy, regulatory, and stakeholder complexities. The potential to build a healthier and stronger future for Americans through biomedical innovations, cutting-edge science, and technology has never been greater. Julie is uniquely equipped to enhance our FDA-related services to help clients navigate the pre- and post-market complexities of the evolving FDA policy and regulatory landscape.”
Tierney joins a team of highly experienced, bipartisan health policy and government affairs consultants, many with significant experience drafting and implementing FDA laws and regulations, and leading private sector life sciences solutions. The Leavitt Partners team includes former health policy directors and FDA subject matter experts from the U.S. Senate Budget Committee, the Senate HELP Committee, the U.S. House Energy and Commerce Committee, and other senior congressional offices. Leavitt Partners, founded by former HHS Secretary Michael O. Leavitt, features former senior political appointees in Democratic and Republican presidential administrations, leaders formerly serving in several U.S. Department of Health and Human Services agencies, and former leaders in the nonprofit and corporate health sectors.
HMA Roundup
Arizona
Arizona Joins Multi-State ArrayRx Consortium to Lower Prescription Drug Costs. The Washington State Health Care Authority announced on August 11, 2025, that Arizona has joined ArrayRx, a multi-state public sector prescription drug consortium founded by Oregon and Washington, aimed at lowering medication costs. Arizona Governor Katie Hobbs signed an executive order to formalize the partnership, allowing all Arizonans, regardless of age or income, to access a free discount card for FDA-approved prescriptions, including mail-order and specialty drugs. The program benefits uninsured, underinsured, or those facing high out-of-pocket costs, and strengthens states’ collective bargaining power to negotiate lower drug prices.
Colorado
Colorado HCPF Director Pledges to Mitigate Medicaid Cuts, Limit Coverage Loss Under H.R.1. Steamboat Pilot & Today reported that Colorado Department of Health Care Policy and Financing (HCPF) executive director Kim Bimestefer pledged to avoid Medicaid cuts and mitigate coverage loss during a virtual roundtable discussing impacts of H.R.1. Bimestefer expressed concerns that hundreds of thousands of Coloradans could be at risk of losing Medicaid due to work requirements as Colorado covers nearly a quarter of the state’s population. The state plans to use lessons learned from the Medicaid unwinding period to keep individuals informed of changes. Colorado is already facing a $750 million budget deficit in the current fiscal year, with costs exacerbated by older individuals seeking long-term care, which will be further strained by the federal changes. Colorado expects to apply to the federal rural health transformation program this fall and could receive up to $100 million in additional funds annually.
Indiana
Indiana Projects Medicaid Cost Surge, Adopts Cost-Saving Actions. Indiana Capital Chronicle reported on August 7, 2025, that Indiana’s Family and Social Services Administration (FSSA) projects per-enrollee Medicaid costs to rise 43 percent for Healthy Indiana Plan (HIP) members and 72 percent for elderly enrollees by 2027, more than doubling state Medicaid appropriations. Going forward, FSSA will assume the state is contributing two percent of its total budget, down from 21 percent in 2025. FSSA is implementing cost-saving measures including halting Medicaid advertising, reducing administrative contracts, cancelling childcare vendor contracts, and reviewing applied behavioral analysis costs. The agency aims to secure about $200 million from the $50 billion rural hospital fund in H.R. 1 and capture one final round of provider tax funding before the law takes effect.
Minnesota
Minnesota Releases Medicaid Enterprise Systems Modernization Strategy RFI. The Minnesota Department of Human Services (DHS) released on July 31, 2025, a request for information (RFI) to gather input for its Medicaid Enterprise Systems (MES) Modernization Strategy. The state seeks to replace and improve the state’s Medicaid technology systems using a modular, flexible, and outcome-driven approach that supports faster implementation, better interoperability between systems, and the ability to adapt to changing program needs. Minnesota is seeking feedback from a wide range of respondents, including technology vendors, healthcare organizations, and other stakeholders, on topics such as system architecture, procurement models, and innovative delivery methods. Responses must be submitted by September 30, 2025.
North Carolina
North Carolina Stopgap Budget Leaves Medicaid $319M Short, Cuts Loom. 828 News Now reported on August 7, 2025, that North Carolina faces a $319 million Medicaid funding shortfall despite a stopgap budget that includes $600 million for the Medicaid rebase and oversight fund, according to North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services (NCDHHS) Secretary Dev Sangvai. NCDHHS warns that addressing the shortfall may require reducing optional benefits or provider rates, which could jeopardize the program’s integrity and threaten initiatives like the Healthy Opportunities Pilots. Governor Josh Stein signed the stopgap measure but called for lawmakers to return with a sustainable, long-term Medicaid funding solution.
Oregon
Oregon Delays Medicaid Reentry Program Due to H.R.1. The Lund Report reported on August 12, 2025, that Oregon has delayed its reentry program to provide Medicaid coverage for incarcerated individuals up to 90-days prior to release following uncertainty around Medicaid funding with the passage of H.R.1. The program was slated to launch in late 2025 for juveniles and early 2026 for adults after the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) had approved the Section 1115 demonstration in July 2024. The Oregon Health Authority stated it would revisit the plan and timeline in the future. CMS approval is set to expire in 2027.
National
MACPAC Releases Issue Brief on Medicaid Financing. The Medicaid and CHIP Payment and Access Commission (MACPAC) released in August 2025, an issue brief providing an updated overview of Medicaid financing. The brief details the distribution of Medicaid spending across eligibility groups, service categories, and delivery systems, noting significant variation in state financing approaches, including the use of provider taxes, intergovernmental transfers, and supplemental payments. The brief also addresses recent trends, such as the impact of the unwinding of continuous coverage, growth in managed care spending, and policy considerations around federal funding caps, financing transparency, and sustainability.
Ten Million Could Lose Coverage Under H.R.1 by 2034, CBO Forecasts. The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) released on August 11, 2025, final projections showing that by 2034, 10 million people could lose health coverage under H.R.1, primarily due to Medicaid work requirements. The CBO estimates 5.3 million people will be uninsured in 2034 and 2.2 million will lose coverage in 2027 from these requirements, largely due to administrative burdens, disproportionately affecting people with disabilities.
Industry News
Aetna to Reduce Medicare Advantage Plans Across 34 States in 2026. Health Payer Specialist reported on August 6, 2025, CVS Health is cutting at least 87 Aetna Medicare Advantage contracts across 34 states for the 2026 open enrollment, reducing about 10 percent of its total Medicare Advantage contracts. Fifty-eight of the plans being cut are preferred provider organizations (PPOs) and 29 are health maintenance organizations (HMOs). States with larger rural populations, namely Alaska, Wyoming, and Utah, will have the most cuts per capita.
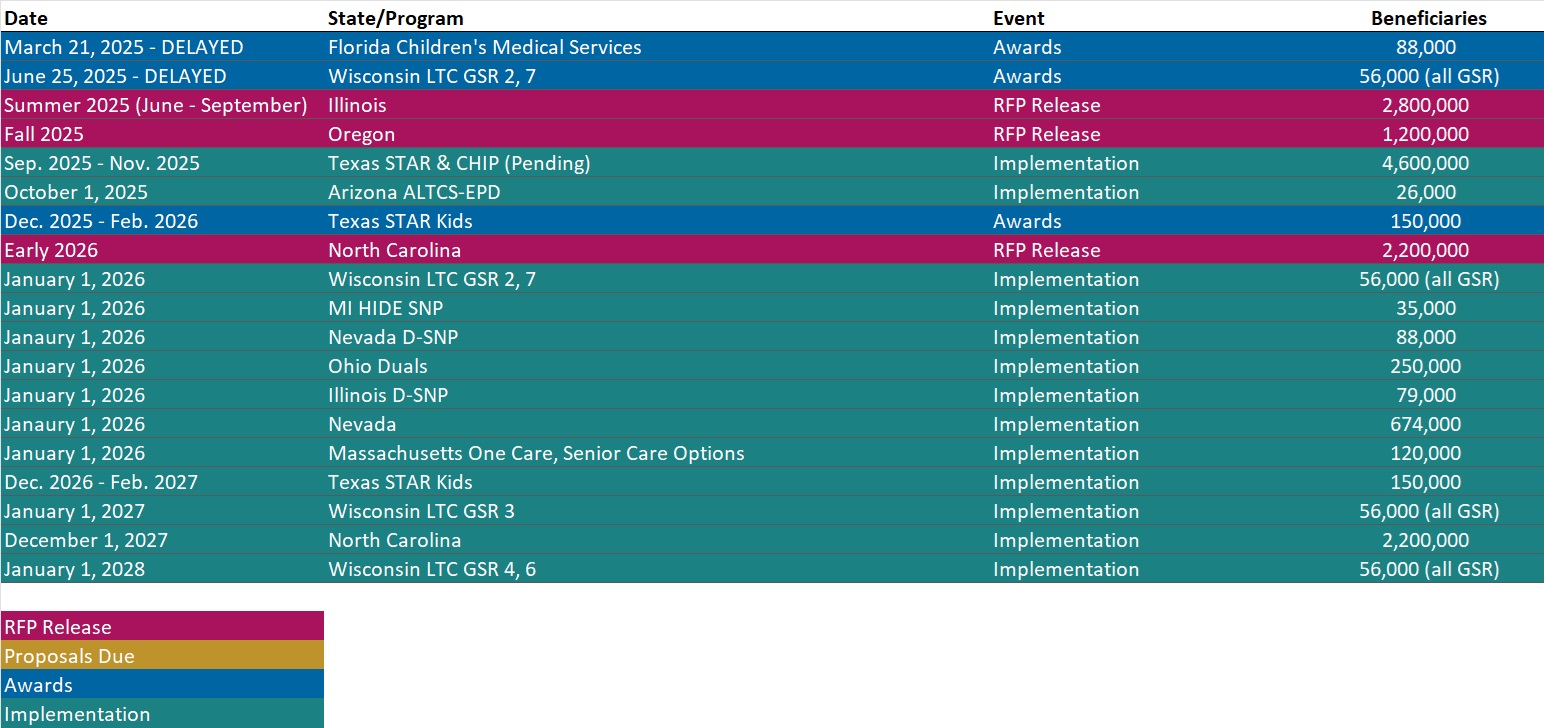
RFP Calendar
Actuaries Corner
The Great Medicare Advantage Contraction Appears Set to Continue. Insurers plan to keep sacrificing MA growth for profitability next year, after second quarter results for Humana and CVS showed the success of the strategy. Editor’s Note: While Humana and CVS are contracting, United gained more than 500,000 Medicare Advantage members in 2025. Now United is planning to exist plans that currently serve more than 600,000 members.
Discover other developments in the Wakely Wire here.
Company Announcements
MCG Press Release
Pennsylvania Department of Human Services Announces Transition to MCG Care Guidelines for Determining Medical Necessity: The Pennsylvania Department of Human Services has adopted the MCG care guidelines as its new standard for determining medical necessity for services, items, procedures, and levels of care provided to Medical Assistance (MA) beneficiaries. Read More
HMA News & Events
HMA Webinar
Work That Works: Creating Sustainable Employment Pathways for Medicaid-Enrolled Communities. Thursday, August 14, 2025, 12 PM ET. As Medicaid increasingly intersects with the social drivers of health, states have a unique opportunity to strengthen economic mobility for Medicaid-enrolled populations through strategic localized employment initiatives in partnership with municipalities, healthcare systems, and managed care providers. This webinar will explore how state Medicaid agencies can lead and support the development of workforce pathways that are sustainable, inclusive, and tailored to the needs of underserved communities.
Wakely Webinar
From Insight to Impact: Measuring What Matters in Care Management. Tuesday, August 26, 2025, 2 PM ET. With care management programs and point solutions continuing to expand across Medicare, Medicaid, and Commercial lines of business, the need for rigorous, data-driven evaluation has never been more urgent. Join us for a practical session on how payers and partners can design and execute credible studies to measure both the financial and member experience impact of their investments. We’ll cover where to start (hint: it begins with your data), introduce analytical frameworks for assessing direct and indirect outcomes, and share lessons from a recent case study—blinded for objectivity. Whether you’re considering how to pursue new opportunities, understanding the landscape, building your first evaluation or refining an existing one, this session offers strategic and tactical guidance for turning good intentions into actionable insights.
NEW THIS WEEK ON HMA INFORMATION SERVICES
(Exclusive Access for HMAIS Subscribers):
HMAIS Medicaid Market Overviews, Reports, and Data
- New State Medicaid Leadership Inventory
- Updated HMA Federal Health Policy Snapshot
- New Medicaid enrollment, RFP documents, and other market intelligence resources for dozens of states
- Updated Oklahoma and South Dakota Overviews
A subscription to HMA Information Services puts a world of Medicaid information at your fingertips, dramatically simplifying market research for strategic planning in healthcare services.
If you’re interested in becoming an HMAIS subscriber, contact Andrea Maresca at [email protected].