This week's roundup:
- In Focus: CMS Releases Advance Notice of Methodological Changes for MA Capitation Rates and Medicare Part C and Part D Payment Policies

- Colorado Hospital Transparency Reports Reveal Increased Operating Expenses, Reimbursements
- Florida House, Senate Consider Bills to Establish Rural Emergency Hospitals
- Georgia Releases PBM RFP in Partnership with Alaska, Montana, and Vermont
- Hawaii Requests Five-year Extension of Hawaii QUEST Integration Waiver
- Iowa Lawmakers Advance Bill to Extend Postpartum Medicaid Coverage to 12 Months
- Minnesota Seeks Section 1115 Medicaid Waiver Amendments to Expand Eligibility for Children
- Mississippi Senate Passes Bill to Streamline Prior Authorization Requests
- Montana Releases Medicaid NEMT Program RFI
- Nevada Medicaid Managed Care RFP Release Expected by January 2025
- New Mexico Receives Federal Approval for Use of Mobile Crisis Intervention Teams
- Cityblock, Fidelis Care Form Partnership to Increase Health Services For New York Medicaid Members
- North Carolina Releases Foster Care Specialty Plan RFP
- North Carolina Medicaid to Launch Behavioral Health IDD Tailored Plans on July 1
- Several States Direct Medicaid Funding to Provide Housing Aid Amidst Disenrollments
- HHS Issues Final Rule Permitting Use of Telehealth for Opioid Treatment Programs
- CMS Outlines Guidelines for Use of Artificial Intelligence in Medicare Advantage
- Cigna Indicates Plans to Grow its Evernorth Health Services Unit
In Focus
CMS Releases Advance Notice of Methodological Changes for MA Capitation Rates and Medicare Part C and Part D Payment Policies
This week, our In Focus section reviews the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Calendar Year (CY) 2025 Advance Notice for the Medicare Advantage (Part C) and Part D Prescription Drug Programs published on January 31, 2024. Alongside the advance notice, CMS published draft CY 2025 Part D Redesign Program Instructions. This guidance includes CY 2025 payment updates as well as additional proposed technical and methodological changes to Medicare Advantage (MA) and Part D. CMS previously released a proposed rule in November 2023 that included proposed policy changes to MA and Part D for CY 2025.
The proposed payment policies signal CMS is working to ensure the stability of MA and Part D programs, while also addressing concerns about the appropriateness of payments to plans. Furthermore, CMS remains highly focused on the impact methodological changes could have on payment to plans that enroll beneficiaries who are dually eligible for Medicare and Medicaid services. Proposals to align quality measures across programs and strengthen the measures used to assess the quality of beneficiary experiences and services provide directional information on CMS’s plans for the forthcoming annual payment rules for 2025.
Following are highlights from the 2025 Advance Notice and Part D Redesign Program Instructions. The deadline for submitting comments is Friday, March 1, 2024. CMS will announce the MA capitation rates and final payment policies for 2025 no later than April 1, 2024.
Payment Impact on MA: CMS is projecting that federal payments to MA plans will increase on average 3.7 percent from 2024 to 2025. The increase reflects multiple factors, including growth rates in underlying costs, change in Star ratings, continued implementation of the new risk adjustment model and fee for service (FFS) normalization, and risk score trends. Actual impacts of the proposed payment policies will vary from plan to plan.
Risk Adjustment: CMS is proposing to continue its three-year phase in of the updated Part C risk adjustment model, first published in the CY 2024 Rate Announcement. In CY 2025, risk scores will be calculated by blending 67 percent of the risk score using the 2024 CMS hierarchical condition categories (HCC) risk adjustment model and 33 percent using the 2020 CMS-HCC risk adjustment model. In addition, the MA risk score trend is being calculated separately under each model, then blended by the respective percentage to determine a CY 2025 risk score trend of 3.86 percent.
CMS is proposing a new methodology for calculating the FFS normalization factor to accurately address the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic without excluding any years of FFS risk scores.
CMS also proposes to apply the statutory minimum MA coding pattern difference adjustment factor of 5.90 percent for CY 2025.
Frailty Adjustment for FIDE SNPs and PACE Organizations. For CY 2025, CMS is proposing to blend the frailty score calculated for fully integrated dual eligible (FIDE) special needs plans (SNPs) consistent with the phase-in of the 2024 CMS-HCC model. The FIDE SNP frailty score is the sum of:
- 33 percent of the score calculated with the 2020 CMS-HCC model frailty factors
- 67 percent of the score calculated with the 2024 CMS-HCC model frailty factors
CMS also intends to use only the full Medicaid frailty factors to calculate frailty scores for FIDE SNP enrollees in order to align with the requirement that FIDE SNPs must have exclusively aligned enrollment, meaning that enrollment in FIDE SNPs will be limited to full-benefit dually eligible individuals, beginning in CY 2025. CMS will use the frailty factors associated with the 2017 CMS-HCC model to calculate frailty scores for Program of All-Inclusive Care for the Elderly (PACE) organizations in CY 2025.
Star Ratings: CMS reiterates its plan to further implement the “universal foundation” of quality measures. CMS first announced this subset of metrics in 2023, with the goal of aligning a core set of metrics across the agency’s programs while continuing to allow for program specific measures. CMS reminds plans that beginning with the 2024 measurement year (2026 Star Ratings), the weight of patients’ experience, complaints, and access measures will be reduced from a weight of four to a weight of two.
CMS proposes several updates and refinements to the Star Ratings program, including:
- Retiring the Care for Older Adults – Pain Assessment (Part C) measure, starting as early as the 2025 measurement year
- Making changes to the Plan Makes Timely Decisions About Appeals and Reviewing Appeals Decisions (Part C) measures for cases submitted electronically to the independent review entity
- Adding Social Need Screening and Intervention (Part C) to the display page for the 2025 Star Ratings and giving notice that National Committee on Quality Assurance (NCQA) is evaluating the potential addition of a utilities insecurity screening and intervention rate for this measure in the future
- Adding Depression Screening and Follow-Up for Adolescents and Adults (Part C) and Adult Immunization Status (Part C) to the display page for the 2026 Star Ratings
- Updating the Members Choosing to Leave the Plan (Part C and D) measure for the 2026 Star Ratings
- Possibly adding the Initiation and Engagement of Substance Use Disorder Treatment (Part C) and Initial Opioid Prescribing for Long Duration (IOP-LD) (Part D) measures
- Revisions to the Care Coordination (Part C) measure, and other changes through future rulemaking
Part D Impact
The advance notice reviews the significant changes to the Part D benefit occurring in 2025 as required in the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). The IRA’s Part D changes effective in CY 2025 include:
- Eliminating the coverage gap phase. A newly defined standard Part D benefit will consist of three phases: annual deductible, initial coverage, and catastrophic coverage. There is no initial coverage limit, and the initial coverage phase will extend to the maximum annual out-of-pocket threshold, after which the catastrophic phase begins.
- Setting the out-of-pocket threshold at $2,000.
- Sunsetting the Coverage Gap Discount Program and implementing of the Manufacturer Discount Program (Discount Program).
- Making changes to the liability of enrollees, plans, manufacturers, and CMS.
- Updating the definition of incurred costs to include, among other categories of costs, supplemental coverage and other health insurance, which was previously excluded. Manufacturer discounts provided under the Discount Program also will be excluded.
- Premium stabilization will continue to be in effect.
CMS is recalibrating the RxHCC risk adjustment model to account for IRA changes and is proposing to calculate separate normalization factors for risk scores used to pay MA-PD plans versus PDPs.
Key Considerations
The impact of the MA risk score trend on payment will vary across individual MA plans. Plans will want to analyze these effects to inform their comments to CMS.
In the advance notice, CMS emphasized the strong growth in the dual SNP market for 2024. This market continues to present growth opportunities. CMS has sought to ensure that changes to payment accuracy better reflect more recent cost and utilization patterns and the risk profile of the sickest and most complex enrollees. Plans will want to consider payment incentives in the context of major policy, reimbursement, and operational changes required to improve integrated care for dually eligible individuals. MA organizations considering becoming FIDE SNPs and wishing to obtain frailty payments in 2025 will need to understand the specific requirements to be eligible for such payments.
The HMA Medicare team will continue to analyze these proposed changes. We have the depth and breadth of expertise to assist with tailored analysis, to model policy impacts across the multiple rules, and to support the drafting of comment letters on this notice.
If you have questions about the contents of CMS’s MA Advance Notice and payment policies and how these would affect MA plans, including SNPs, providers, and Medicare beneficiaries, contact Julie Faulhaber (jfaulhaber@healthmanagement.com), Amy Bassano (abassano@healthmanagement.com), or Andrea Maresca (amaresca@healthmanagement.com).
HMA Roundup
Colorado
Colorado Hospital Transparency Reports Reveal Increased Operating Expenses, Reimbursements. The Colorado Department of Health Care Policy & Financing released on February 5, 2024, mandatory reports analyzing hospital financials and pricing transparency. Some findings from the 2024 reports include that net patient revenues in the state are returning to pre-pandemic levels, tax exempt hospitals’ community investments rose by 13 percent in fiscal year 2021 and 55 percent of funding was directed to addressing social determinants of health, and the hospital assessment provided an additional $464 million in reimbursement to hospital providers and funding for Medicaid coverage without increasing Colorado’s General Fund expenditures. Read More
Florida
Florida House, Senate Consider Bills to Establish Rural Emergency Hospitals. Health News Florida reported on February 4, 2024, that the Florida House Select Committee on Health Innovation approved a bill, sponsored by Representative Jason Shoaf (R-Port St. Joe), that would establish a category of rural emergency hospitals in the state that could receive Medicare payments to provide emergency services, observation care, and outpatient services. The bill, intended to increase health access in rural areas, awaits further House review. Senator Corey Simon (R-Tallahassee) sponsored a Senate version of the bill which has been approved by the Senate Health Policy Committee. Read More
Florida Files Lawsuit Over CMS Ban on Disenrolling CHIP Beneficiaries. POLITICO Pro reported on February 1, 2024, that Florida Governor Ron DeSantis has filed a lawsuit against the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), which prohibited the state from removing children from the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) funded program, KidCare, if parents stopped paying the required premiums. Specifically, the state is seeking a preliminary injunction and stated that CMS has violated the federal Administrative Procedure Act. KidCare serves more than 119,000 children from families with incomes above the maximum threshold for Medicaid eligibility. Read More
Florida Advocacy Group Pushes to Include Medicaid Expansion on 2026 Ballot. The Tallahassee Democrat reported on February 1, 2024, that advocacy group Florida Decides Healthcare has launched an effort to raise a minimum of $12 million and collect nearly 1 million signatures to place Medicaid expansion on the 2026 ballot. If the measure is approved and passed by a minimum of 60 percent of voters, the state’s constitution would be amended to include Medicaid expansion. Medicaid expansion would expand coverage to approximately 1.4 million individuals. Read More
Georgia
Georgia Sues Federal Government to Extend Limited Expansion with Work Requirements. The Georgia Recorder reported February 2, 2024, that Georgia has sued the federal government in an effort to keep the Georgia Pathways to Coverage limited Medicaid expansion with work requirements running until 2028. The suit, filed in U.S. District Court, claims that the Biden administration’s attempt to try to revoke the program’s work requirement delayed implementation, which reduced the approved five-year term to just over two years. The state is asking the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to extend its Georgia Pathways to Coverage existing agreement; however, the state has not yet submitted a formal extension. The program is set to expire at the end of September 2025. Read More
Georgia Releases PBM RFP in Partnership with Alaska, Montana, and Vermont. The Georgia Department of Administrative Services released on February 1, 2024, a request for proposals (RFP), in partnership with NASPO ValuePoint cooperative purchasing program, for one or more pharmacy benefit manager (PBM) vendors to serve Georgia, Alaska, Montana, and Vermont’s fee-for-service Medicaid pharmacy program. Georgia, the lead state, will evaluate responses, and establish master agreements with the support and assistance of a multistate sourcing team composed of individuals from other member states. The initial contract term will run for one year and the lead state will have nine, one-year options to renew the master agreement. Proposals are due by March 28. Read More
Hawaii
Hawaii Requests Five-year Extension of Hawaii QUEST Integration Waiver. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services announced on February 5, 2024, that the Hawaii Department of Human Services has applied for a five-year extension of its Section 1115 Hawaii QUEST Integration waiver through July 31, 2029. The demonstration extension proposal includes continuous eligibility for children ages 0 through 5, continuous two-year eligibility for children ages 6 through 18, pre-release services for justice-involved individuals, nutrition supports, contingency management, rental assistance expansion, and medical respite to the state’s Community Integration Services program. Public comments will be accepted through March 6. Read More
Idaho
Idaho House Committee Kills Bill that Could Repeal Medicaid Expansion. The Idaho Capital Sun reported on February 1, 2024, that the Idaho House Health and Welfare Committee voted to hold a bill that could have repealed Medicaid expansion by October 2025 in committee, preventing its advancement to the House floor. The bill, sponsored by Representative Jordan Redman (R-Coeur d’Alene), would have repealed expansion if 11 new requirements had not been met by July 2025 and would have capped Medicaid expansion enrollment at 50,000 people or the total number of enrollees classified as disabled or aged 65 and above. Read More
Indiana
Indiana Lieutenant Governor Calls for Audit of Family, Social Services Administration Following $1 Billion Medicaid Shortfall. The Indiana Capital Chronicle reported on February 6, 2024, that Indiana Lieutenant Governor Suzanne Crouch called for an independent, outside audit of the Family and Social Services Administration (FSSA) following the organization’s announcement of a $1 billion Medicaid spending shortfall. The shortfall led FSSA to push for $300 million in program cuts, including removing compensation for parents serving as caregivers of medically complex children. The state’s General Assembly and Governor Eric Holcomb rejected Crouch’s previous request for a pause to the proposed cuts. Read More
Indiana Legislature Kills Bills that Would Clarify Medicaid HCBS Waivers, Eliminate Prior Authorization. The Indiana Capital Chronicle reported on February 2, 2024, that the Indiana legislature killed bills that would have clarified Medicaid home and community-based services waivers and eliminated most prior authorization requests. HB 1386, sponsored by Representative Bradford Barrett (R-Richmond), died in the House following the addition of amendments seeking transparency and accountability regarding the state’s $1 billion Medicaid funding shortfall. SB 3, sponsored by Senators Tyler Johnson (R-Leo), Ed Charbonneau (R-Valparaiso), and Chris Garten (R-Charlestown), died in the Senate after legislators raised concerns about its potential to raise health care costs by eliminating the majority of prior authorizations. Read More
Iowa
Iowa Lawmakers Advance Bill to Extend Postpartum Medicaid Coverage to 12 Months. The Iowa Capital Dispatch reported on February 5, 2024, that the Iowa Senate Health and Human Services Subcommittee has advanced a bill to extend postpartum Medicaid coverage from 60 days to one year. The bill proposes to limit eligibility for Medicaid coverage of birth and postpartum care to 215 percent of the federal poverty level from 380 percent under current law. The bill would also include coverage for newborns at 302 percent of the federal poverty level through the Healthy and Well Kids in Iowa (Hawki) program. Read More
Iowa House Subcommittee Passes Bill Requiring Additional Oversight of Temporary Medical Staffing Agencies. Iowa Public Radio reported on February 1, 2024, that the Iowa House Health and Human Services subcommittee advanced a bill that would require additional oversight of staffing agencies that supply temporary healthcare workers, aiming to improve the state’s staffing shortages within nursing homes and hospitals. The bill would require agencies to register with the Iowa Department of Health and Human Services, which would oversee new regulations such as wage caps that limit the amount temporary workers can make. Read More
Kentucky
Kentucky Senate Committee Advances Bill to Cover Midwife Services Under Medicaid. WKMS reported on January 31, 2024, that the Kentucky Senate Committee on Families and Children advanced legislation that would allow Medicaid coverage for midwife services. Licensed midwives would be able to offer prenatal, postpartum, and labor and delivery services. Read More
Maine
Maine to Increase Hospital Medicaid Reimbursement. The Portland Press Herald reported on February 6, 2024, that the Maine Department of Health and Human Services has agreed to increase Medicaid reimbursement rates for all in-state hospitals, with the exception of four psychiatric hospitals. Under the agreement, funding will come from $90.3 million allocated to the upcoming state supplemental budget on July 1. The agreement is subject to approval by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Read More
Maryland
Maryland Disenrolls 58,000 Medicaid Beneficiaries During December Redeterminations. DCist reported on February 5, 2024, that Maryland disenrolled a total of more than 245,000 Medicaid beneficiaries in 2023. In December, the state disenrolled 58,016, including 51,249 for procedural reasons and 6,767 for ineligibility. Read More
Minnesota
Minnesota Seeks Section 1115 Medicaid Waiver Amendments to Expand Eligibility for Children. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services announced on February 5, 2024, that the Minnesota Department of Human Services has requested two amendments to its Section 1115 Prepaid Medical Assistance Project Plus Medicaid waiver aimed at expanding eligibility for children. The first amendment would provide Medicaid eligibility for former foster care youth who turned 18 prior to January 1, 2023, and are under the age of 26. A separate amendment would allow 12-months of continuous Medicaid eligibility for 19 and 20-year-olds; and continuous eligibility for eligible children up to age six. Public comments will be accepted through March 6. Read More
Report Examines Public Option Cost, Funding in 2027. MPR News reported on February 1, 2024, that the Minnesota Department of Human Services released a report on projected public option cost and funding in 2027, predicting that this expansion of the Medicaid program would cost the state up to $364 million annually and would expand services to an additional 151,000 individuals. The report also outlined a second model which would be a three tiered plan available through the state’s health insurance marketplace, costing the state between $86-187 million annually. Read More
Mississippi
Mississippi Democrats To File Multi-component Medicaid Expansion Bill. Mississippi Today reported on February 5, 2024, that Mississippi Democratic representatives plan to file a bill that would expand Medicaid eligibility to all adults and offer a private insurance option for adults with no children who make up to 200 percent of the federal poverty level. Additionally, individuals employed and making between 96 percent and 200 percent of the federal poverty level could have their insurance premiums covered at varying degrees. It is estimated that Medicaid expansion would cover an additional 250,000 individuals. Read More
Mississippi Senate Passes Bill to Streamline Prior Authorization Requests. Mississippi Today reported on February 2, 2024, that the Mississippi Senate passed a bill requiring insurance companies to create a portal or website by January 2025 for doctors to submit prior authorization applications. Insurance companies would have 24 hours to process authorizations related to urgent services or procedures that can help treat someone in intense pain and five days for non-urgent services. Read More
House Passes Bill to Allow 60-days of Prenatal Presumptive Medicaid Eligibility. The Associated Press reported on January 31, 2024, that the Mississippi House passed a bill to allow up to 60 days of prenatal presumptive Medicaid eligibility, making it easier for expectant mothers to access timely prenatal care. If enacted, the bill would take effect on July 1, 2024. Read More
Montana
Montana Awards Maximus Contract for Employment and Training Services. The Montana Department of Public Health and Human Services announced on January 31, 2024, that Maximus US Services has been awarded to provide statewide Employment and Training Services to participants in the state’s Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program and the Temporary Assistance for Needy Families cash assistance program. The contract is set to begin on July 1, and public comments can be made through February 7. Read More
Montana Releases Medicaid NEMT Program RFI. The Montana Department of Public Health and Human Services released on January 31, 2024, a request for information (RFI) regarding the state’s Medicaid non-emergency medical transportation (NEMT) program. The program covers about 292,000 Medicaid members. Responses must be submitted by February 9. Read More
Nevada
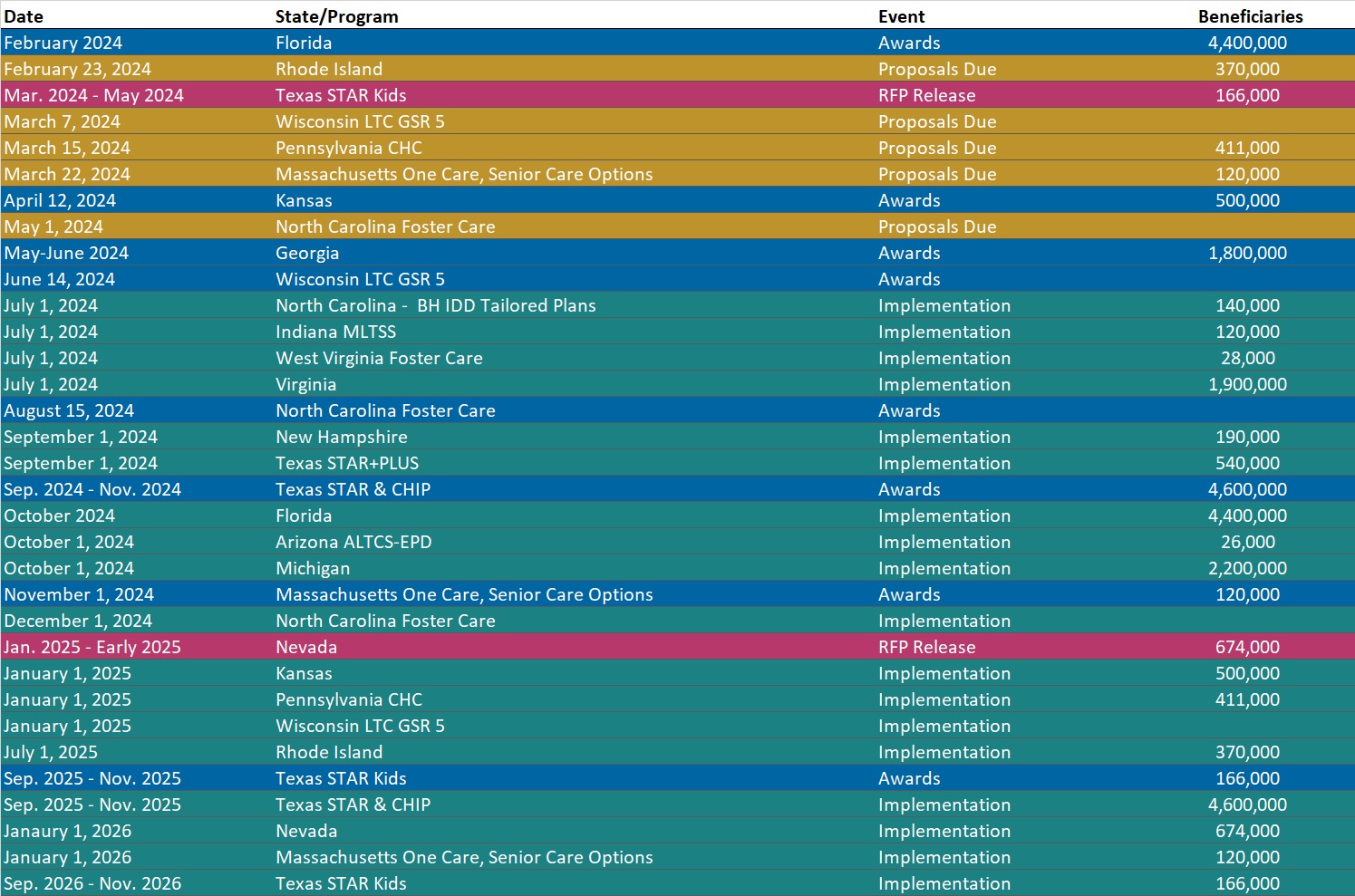
Nevada Medicaid Managed Care RFP Release Expected by January 2025. The Nevada Division of Health Care Financing and Policy announced on January 18, 2024, in a stakeholder presentation that the statewide Medicaid managed care request for proposals (RFP) is expected by January 2025 and contract implementation will begin January 1, 2026. Read More
New Mexico
New Mexico Receives Federal Approval for Use of Mobile Crisis Intervention Teams. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services announced on February 6, 2024, that it has approved a proposal from New Mexico to provide Medicaid crisis services using community-based mobile crisis intervention teams. There are now 15 states that have expanded access to community-based mental health and substance use crisis care through the American Rescue Plan. Read More
New York
Cityblock, Fidelis Care Form Partnership to Increase Health Services for Medicaid Members. Cityblock Health announced on February 7, 2024, that it will be partnering with Centene/Fidelis Care to provide community-based care to Medicaid members in New York City and Long Island living with complex medical and behavioral health conditions. Fidelis Care’s Medicaid and HealthierLife – Health and Recovery Plan members with complex needs will have access to Cityblock’s integrated primary care, behavioral health, and social care services. Read More
New York Caucus Requests Reimposition of Medicaid Quality Incentive Program Funding. Spectrum Local News reported on February 5, 2024, that New York members of the Black, Puerto Rican, Hispanic and Asian Legislative Caucus are asking that Medicaid Quality Incentive Program (QIP) funding be restored in the state budget proposal, after being cut by Governor Kathy Hochul. Caucus members are requesting $268 million in funding for fiscal 2025, after it was previously funded at $111 million last year. The QIP program serves as a deferred payment program for health providers when they take action to close gaps in care for patients and improve access. Read More
Senate Passes Legislation Allowing State to Manufacture Generic Drugs, Lowering Spending. Crain’s New York Business reported on January 31, 2024, that the New York Senate advanced legislation that would authorize the state Department of Health (DOH) to contract with private companies to manufacture generic drugs in an effort to lower prescription drug prices. Under the New York State Affordable Drug Manufacturing Act, DOH and the health commissioner would assess which drugs make good candidates for state manufacturing based on Medicaid population usage and how much a state-manufactured alternative could reduce spending. Read More
North Carolina
North Carolina Releases Foster Care Specialty Plan RFP. The North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services released on February 7, 2024, a request for proposals (RFP) for the new Children and Families Specialty Plan (CFSP), a single, statewide plan for children, youth, and families served by the child welfare system. The CFSP is one of four types of integrated Medicaid managed care plans developed to transition North Carolina’s Medicaid program from fee-for-service to managed care. The plan will provide physical health, behavioral health, intellectual and developmental disability, long-term care, and pharmacy services. Proposals are due May 1 and awards are expected August 15. Contracts will run December 1, 2024, through June 30, 2028, with one additional one-year renewal option. Read More.
North Carolina Medicaid to Launch Behavioral Health IDD Tailored Plans on July 1. NC Newsline reported on February 6, 2024, that North Carolina will begin implementation of Behavioral Health and Intellectual/Developmental Disabilities (BH IDD) Tailored Plans on July 1. Tailored plans will be provided through the awarded Local Management Entity-Managed Care Organizations (LME-MCOs) Alliance Health, Partners Health Management, Trillium Health Resources, and Vaya Health. Implementation has been delayed multiple times since 2022, most recently from October 2023. As a result, the state issued a directive last year to dissolve the Sandhills Center and consolidate Eastpointe and Trillium Health Resources to hasten the delayed rollout. The tailored plans are expected to cover about 160,000 beneficiaries. Read More
Texas
Texas Advocates File Federal Complaint Over Deloitte Medicaid Eligibility Software Errors. The Texas Tribune reported on January 31, 2024, that health care advocates filed a complaint with the Federal Trade Commission, claiming that Deloitte Consulting LLP caused wrongful Medicaid disenrollments in Texas due to errors in their Medicaid eligibility system. Deloitte stated that the complaint is without merit. Read More
Vermont
Vermont House Considers Bill to Expand Medicaid for Pregnant People, Young Adults. Vermont Public reported on February 1, 2024, that the Vermont House is considering a bill sponsored by Representative Lori Houghton (D-Essex Junction) and several co-sponsors, that would expand Medicaid coverage for pregnant people and individuals between the ages of 19 and 26 who earn up to 312 percent of the federal poverty level beginning in 2025. The bill also calls for an analysis to determine how Medicaid could be expanded for all adults and increase Medicaid reimbursement rates for health care providers. The bill has been referred to the House Committee on Health Care. Read More
West Virignia
West Virginia Bureau of Medical Services Selects New Financial Management Services Vendor. WV News reported on February 1, 2024, that the West Virginia Department of Human Services’ Bureau for Medical Services has selected Palco to provide financial management services effective April 1. Specifically, Palco will serve more than 4,900 Medicaid beneficiaries receiving home and community-based services via three waiver programs in the Personal Options program. Palco will replace the current vendor, Public Partnerships, and is working with the department to launch an informational campaign to inform participants and employers about the transition. Read More
House Finance Committee Passes Bill to Increase Tax Rates on Select Hospitals. ABC 4 WOAY reported on January 31, 2024, that the West Virginia House of Delegates Finance Committee passed a bill, sponsored by Representative Matthew Rohrbach (R-Cabell), that would increase tax rates on certain hospitals to the maximum amount permitted by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. The bill aims to address the state’s $114 million Medicaid budget shortfall and will next receive a second reading in the House. Read More
National
CMS Outlines Guidelines for Use of Artificial Intelligence in Medicare Advantage. Modern Healthcare reported on February 6, 2024, that the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) informed Medicare Advantage (MA) insurers that artificial intelligence (AI) may be utilized to make coverage decisions but may not override benefits rules and medical necessity standards. CMS specified that patient-specific factors must still be considered in coverage decisions and that insurers should ensure that the use of AI does not exacerbate health inequities. Several MA insurers, including UnitedHealth Group, Humana, and Cigna, are currently involved in lawsuits alleging that they used AI to decline coverage. Read More
Medicaid Enrollment Is Down 9.5 Million Halfway Through Unwinding Period, KFF Finds. KFF Health News reported on February 7, 2024, that total Medicaid enrollment has decreased by a net total of approximately 9.5 million since the beginning of the Medicaid eligibility redeterminations process. By the end of the process, Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program enrollment is expected to return to pre-pandemic levels, totaling approximately 71 million. Thus far, states have disenrolled more than 16 million beneficiaries, while simultaneously re-enrolling and granting first-time coverage to millions. Read More
Centene Loses Appeal to Keep Tricare West Region Contract. Health Payer Specialist reported on February 7, 2024, that Centene’s appeal of the $65 billion Tricare western region contract award to TriWest Healthcare Alliance was rejected by the U.S. Court of Federal Claims. The Government Accountability Office previously upheld the decision in August. Read More
Increased Medicaid Drug Spending Was Driven by Specialty Drugs in 2021, MACPAC Finds. The Medicaid and CHIP Payment and Access Commission (MACPAC) released in February 2024, an issue brief that demonstrated that Medicaid drug spending grew in 2021, mainly due to high-cost specialty drugs, and totaled $38.1 billion in net drug spending. High-cost specialty medications include cell and gene therapies and generally have low rebates and high launch prices. MACPAC recommended increasing Medicaid rebates for drugs until their clinical benefit is verified and permitting states to require evidence on a drug’s benefits for Medicaid populations when granting Medicare coverage. Read More
Several States Direct Medicaid Funding to Provide Housing Aid Amidst Disenrollments. KFF Health News reported on February 6, 2024, that at least 19 states are utilizing Medicaid funding to provide housing services to address the homelessness epidemic. Rates of homelessness have increased and a recent Health Affairs study found that Medicaid disenrollments, which have similarly increased, may result in more evictions. Read More
HHS Issues Final Rule Permitting Use of Telehealth for Opioid Treatment Programs. Modern Healthcare reported on February 1, 2024, that the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) released a final rule that allows opioid treatment programs to initiate buprenorphine and methadone treatment via telehealth. Following telehealth evaluations, practitioners may order treatment medications as indicated. The rule, which makes permanent temporary flexibilities first issued by SAMHSA in spring 2020, will go into effect on April 2. Read More
Biden Administration Initiates Medicare Prescription Drug Price Negotiations for 10 Drugs. USA Today reported on February 1, 2024, that the Biden Administration initiated Medicare drug price negotiations with manufacturers of 10 widely prescribed drugs – Eliquis, Jardiance, Xarelto, Januvia, Farxiga, Entresto, Enbrel, Imbruvica, Stelara, and the insulins Fiasp and NovoLog. Negotiations are expected to continue through the spring and summer. Final prices will be announced September 1 and take effect January 2026. Price negotiations for the 10 drugs, which comprised approximately 20 percent of Medicare Part D prescription drug spending in the last year, are expected to result in $98.5 billion in savings over a decade. Read More
OIG to Audit CMS Oversight of Third-party Nursing Home Surveyors. JD Supra reported on January 31, 2024, that the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Office of Inspector General (OIG) will audit the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS) nursing home survey practices and release findings in 2025. Specifically, OIG will examine whether CMS effectively monitors the third-party contractors that states utilize to conduct federally mandated routine surveys of skilled nursing facilities at least every 15 months. Previous reviews of nursing homes have found that several routine surveys were backlogged. Read More
Industry News
Tenet Health Closes Deal to Sell Three SC-based Hospitals to Novant Health. Modern Healthcare reported on February 1, 2024, that Tenet Healthcare closed a deal to sell three South Carolina-based hospitals to Novant Health for $2.4 billion in cash. The transaction includes Coastal Carolina Hospital in Jasper County, Hilton Head Hospital in Beaufort County, East Cooper Medical Center in Charleston County, and other affiliated physician practices and hospital operations. As part of the deal, Tenet’s Conifer Health Solutions subsidiary will enter into a 15-year contract to handle revenue cycle management for the South Carolina hospitals. Read More
Cigna Indicates Plans to Grow its Evernorth Health Services Unit. Modern Healthcare reported on February 2, 2024, that Cigna has indicated plans to grow its Evernorth Health Services unit, which provides care delivery, benefits services, and pharmacy services, including the Express Scripts pharmacy benefit manager. Cigna will focus on expanding health plan partners and investing in digital-first and data-led capabilities. Cigna expects to continue to offer pharmacy benefits to Medicare Advantage (MA) plans, despite the company’s recent sale of its MA business to Health Care Service Corporation. Read More