This week, our In Focus section examines governors’ healthcare priorities from their 2025 State of the State addresses. This article highlights common themes in addresses delivered between January 6, 2025, and January 16, 2025, and delves into specific proposals in Georgia, Iowa, New York, and Oregon, as analyzed in the Health Management Associates (HMA), Information Services (HMAIS) interim report, 2025 State of the State Overview.
State of the States in the Current Environment
Governors use their State of the State addresses to outline their priorities for the year, giving insight into the agendas and initiatives that their executive branches may pursue independently or in collaboration with their state legislature. These priorities often are informed by the status of the state’s budget, with some governors advancing healthcare proposals that will address budget deficits and others seeking to invest in services and workforce initiatives.
Monitoring governors’ policy priorities and initiatives is especially important in 2025 given the changing federal landscape. The transition in both the administration and Congress will require state leaders to carefully consider the risks and opportunities. As detailed below, governors’ responses will unfold differently across states and markets.
Common Threads
In all, 24 governors delivered a State of the State Address between January 6, 2025, and January 16, 2025. Many gubernatorial leaders have similar areas of priority and concern, with some continuing multiyear initiatives to address unmet behavioral health needs and control healthcare costs. Table 1 identifies the themes emerging from the first group of addresses.
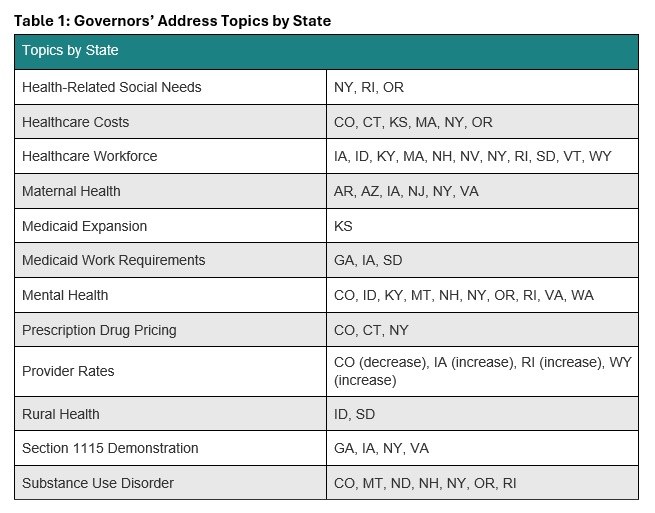
Governors also are considering possible policy changes under the new Trump Administration. For example, some governors reported that their state is looking to strengthen or add Medicaid work requirements to their programs, resuming initiatives that were initially pursued during the first Trump Administration. Though not directly related to healthcare, governors’ decisions to mirror President Trump’s Department of Government Efficiency, with Iowa as an example, could indirectly affect local programs and markets. Other states are considering the implications of possible changes to federal Medicaid funding. A deeper look into the priorities in Georgia, Iowa, New York, and Oregon follows.
Georgia
Gov. Brian Kemp delivered Georgia’s State of the State address on January 16, 2025, during which he focused his healthcare remarks on the state’s Pathways to Coverage Section 1115 demonstration. Georgia’s waiver extends Medicaid coverage to able-bodied adults who earn up to the federal poverty level if they meet certain work requirements. The governor emphasized that he intends to work with the Trump Administration to further advance innovative approaches to healthcare access.
Governor Kemp stated that his administration is making it easier to apply for Medicaid coverage and will submit an amendment to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) that would extend the Pathways demonstration for five years beyond the current expiration date of September 30, 2025. The state plans to request several changes to the demonstration, including:
- Changing the reporting requirements for qualified work activities
- Adding more activities that qualify for program eligibility
- Adding a retroactive coverage policy
- Removing premiums and Member Reports Accounts
The governor’s proposed fiscal year (FY) 2026 budget includes $324 million to fully fund projected Medicaid enrollment and utilization growth and $36 million in additional support for pharmacy benefits, including recently approved gene therapy treatments for sickle cell disease.
Iowa
Iowa Gov. Kim Reynolds delivered the Condition of the State Address on January 14, 2025, during which she called for increased Medicaid reimbursement rates for OB/GYNs and primary care physicians who provide care to people with complex pregnancy cases, as well as certified nurse midwives. The governor also said she was in favor of adding doula services as a covered Medicaid benefit. Governor Reynolds is one of several governors who have announced plans to pursue a Section 1115 demonstration for Medicaid work requirements for able-bodied adults.
Governor Reynolds’s proposed FY 2026 budget includes investing $642,000 in newly unbundled Medicaid maternal rates, and more than double investments in five existing state healthcare loan repayment programs. The governor also proposes to establish a Medicaid Graduate Medical Education enhanced payment to draw down more than $150 million in federal dollars for more residency spots in Iowa’s teaching hospitals.
New York
New York Gov. Kathy Hochul delivered her State of the State Address on January 14, 2025, at which time she also released a State of the State Book. Addressing behavioral health is one of her chief priorities, and proposals include:
- Allowing more involuntary commitments for people with severe mental illness
- Developing programs to support youth mental health through after school programs
- Expanding peer support programs
- Improving the diagnostic process for children with complex needs
- Supporting mental wellness in historically marginalized neighborhoods
- Expanding Mobile Medication Units to bring opioid treatments to underserved areas
Governor Hochul intends to expand support for the state’s healthcare safety net. This part of her agenda would provide financial assistance to struggling medical facilities and hospitals through expansion of the state’s Safety Net Transformation Program and participation in the US Food and Drug Administration’s program that allows states to import lower-cost drugs from Canada.
The governor’s proposed $252 billion budget for FY 2026 would allocate $35.4 billion for the state Health Department’s Medicaid budget—a 14 percent increase from last year. Governor Hochul plans to offset some of the spending hike with revenue from the newly approved managed care organization tax, which is expected to raise $3.7 billion to help balance the state budget over three years.
Oregon
Gov. Tina Kotek delivered Oregon’s 2025 State of the State Address on January 13, 2025. The governor has a significant focus on mental health and substance use disorder treatment, as well as housing as an HRSN. Governor Kotek wants to strengthen the behavioral health system and proposed adding new treatment beds, increasing treatment capacity, eliminating backlogs at the state’s health licensing boards to improve access to qualified counselors, improving the provider pipeline, and increasing worker retention. During her speech, the governor also called for improved frontend care coordination to decrease the overflow of people at the Oregon State Hospital.
In addition, the governor intends to work toward improving care for the civil commitment population (i.e., people who are involuntarily detained in a psychiatric hospital) by dedicating permanent supportive housing funds to expanded residences with onsite services. Governor Kotek has directed her team to develop a new intensive permanent supportive housing model to more effectively support people with serious mental health needs.
Governor Kotek’s proposed budget for the 2025−2027 biennium includes $39.6 billion for the Oregon Health Authority, representing a 10.4 percent increase from the approved budget for 2023−2025. This budget includes $29.6 billion for the state Medicaid program and $1.6 billion for the Behavioral Health Division, in addition to $732.4 million for the division from the General Fund.
Connect With Us
HMAIS has prepared a comprehensive report summarizing each State of the State Address, which is available to HMAIS subscribers. The report also examines proposed budgets, highlighting key financial commitments and allocations that underscore these priorities for the upcoming year. The first iteration of the report covers AR, AZ, CO, CT, GA, IA, ID, KS, KY, MA, MT, ND, NE, NH, NJ, NV, NY, OR, RI, SD, VA, VT, WA, and WY. The document will be updated periodically as speeches occur.
Contact our experts below for more information about the report or to connect with one of HMA’s state policy and market experts.






