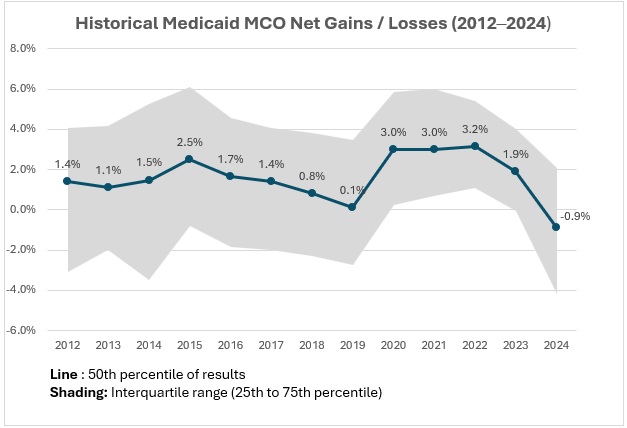
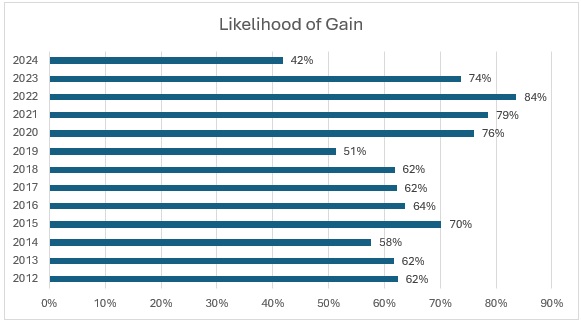
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has officially opened the application window for the Rural Health Transformation Program (RHTP)—a $50 billion federal initiative designed to stabilize and transform rural health systems across the country. This one-time opportunity allows states to submit a comprehensive plan that could redefine how rural communities access care, manage chronic conditions, and sustain their healthcare infrastructure.
As outlined in our earlier In Focus article, States Begin to Engage with the Rural Health Transformation Program, RHTP represents one of the most significant federal investments in rural health in decades.
Applications must be signed by governors and submitted by November 5, 2025, and awards are expected by December 31, 2025, providing states with a very narrow window to act.
The remainder of this article explains key aspects of the RHTP application, including the evaluation and scoring aspects. Notably, the structure of the scoring system will reward states that are already aligned with these federal priorities, as well as those willing to implement new initiatives or make state policy changes to achieve alignment.
Program Overview and Funding Structure
Created under HR.1, the 2025 Budget Reconciliation Act, the RHTP allocates $10 billion annually from federal fiscal year (FY) 2026 to FY 2030, totaling $50 billion over five years. Funding is split into two tranches:
- Tranche 1 (Baseline funding): $25 billion distributed evenly across all states with approved applications.
- Tranche 2 (Workload funding): $25 billion distributed based on CMS scoring criteria, which include:
- The percentage of the state population in rural census tracts
- The proportion of rural health facilities in the state
- The financial and operational status of hospitals
- Other factors explained in the RHTP application notice
States must submit a single, one-time application that covers the full five-year period. Stand-alone provider applications will be declined. Hence, states must coordinate across agencies, providers, and stakeholders to develop a unified transformation strategy.
Importantly, this award is not a grant; rather, it is a cooperative funding agreement, which means CMS will play an active role in oversight and collaboration. States must be prepared to meet higher standards of accountability, transparency, and performance monitoring. According to the RHTP application, continued funding requires states to demonstrate satisfactory progress toward implementing their plan.
Application Requirements and Strategic Priorities
To be eligible for funding, states must submit a Rural Transformation Plan that addresses eight core priorities as follows:

Within these core priorities, state plans must propose activities that address several specific issues.
Technical Factor Weighting for Workload Funding Reflects Federal Policy Priorities
CMS outlines the eligibility criteria for baseline funding and the scoring components for workload funding. Baseline funds will be distributed equally among states, while workload funding will be based on each state’s rural facility and population score as well as their technical score. Evaluators will score technical factors based on state policy actions and initiative-based plans for each state.
The technical factors, and the weighting of these factors, in the RHTP application are not just neutral scoring mechanisms; rather, they are closely linked to the Trump Administration’s health policy priorities.
- Weighting Structure: The RHTP funding is split evenly between baseline funding (50%) and workload funding (50%). Although baseline funding ensures all states receive support, the workload funding is directly tied to technical scores that reflect how well a state’s plan aligns with federal objectives and demonstrates readiness to implement transformative change that furthers federal objectives.
- Scoring Criteria: Technical factors, such as rural population share, facility density, hospital financial status, scope of proposed activities, administrative capacity, stakeholder engagement, evaluation framework, and especially alignment with federal priorities, all contribute to the overall score. States that have already adopted or are willing to adopt federal policy priorities are positioned to score higher and receive more funding.
- Annual Recalculation: CMS will recalculate each state’s technical score and workload funding annually to incentivize ongoing alignment with federal priorities and measurable progress toward transformation goals.
- Alignment with Federal Priorities: One of the explicit scoring factors is “Alignment with Federal Priorities,” which measures the degree to which a state’s plan supports CMS goals for rural health transformation and sustainability. Under the Trump Administration, these priorities may include promoting value-based payment models, encouraging technology adoption, advancing adoption of Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) food restriction waivers that prohibit the purchase of non-nutritious items, availability of integrated care plans for the Medicare-Medicare dually eligible population, reporting of full Medicaid T-MSIS data, and align policies with federal guidance on short-term limited duration insurance plans.
Preparing for What Happens Next: Implications for States, Providers, and Health Plans
The RHTP offers a rare opportunity to reshape rural healthcare. But success will require strategic coordination and a commitment to long-term change. States in the short and long term should consider include:
- Identifying stakeholders who will be involved: Hospitals, rural health clinics, federally qualified health centers (FQHCs), behavioral health providers, and community organizations must be part of the planning process.
- Reexamining priorities: States will need to reconcile competing needs across regions and provider types, balancing infrastructure investments with service delivery redesign.
- Understanding infrastructure needs to support their project: Technology, workforce, and models of care must be strengthened to support long-term transformation.
- Designing evaluation frameworks: States must include robust performance monitoring and reporting mechanisms to meet CMS expectations and secure future funding.
Providers and other stakeholders should also prepare to align with state strategies. Examples include:
- Participating in regional partnerships
- Adopting new care models and payment arrangements
- Investing in technology and workforce development
- Contributing data and insights to support evaluation efforts
The scoring structure also incentivizes states that may not yet be fully aligned to implement new initiatives or make policy changes that would improve their technical scores and secure greater funding. States and their partners will need to be united on the goals and initiatives, disciplined about implementing and evaluating the plans based on data informed reports, nimble and willing to make strategic pivots based on feedback and experiences.
Connect With Us
States that are already aligned with Trump Administration priorities—such as those with established value-based payment models, short-term limited duration plan options, preferred technology infrastructure, or strong rural hospital support policies—are positioned to be rewarded in the scoring and funding process.
Health Management Associates (HMA), is actively supporting states in developing compliant and compelling RHTP applications. Our advisory services include:
- Strategic assessments and stakeholder engagement
- Program design and grant writing
- Implementation support and technical assistance
- Actuarial support
- Evaluation and performance monitoring
We help clients navigate the complexities of federal funding, align transformation goals with community needs, and build sustainable models for rural care delivery. For details about the RHTP, including the HMAIS State Action Tracker, contact HMA experts below.