This week, our In Focus section reviews priorities outlined in recent State of the State addresses, building on an earlier article: A Closer Look at Gubernatorial Healthcare Priorities: 2025 State of the State Address Overview. We examine specific proposals from the governors of Illinois, Indiana, New Mexico, and South Carolina, as detailed in the Health Management Associates Information Services (HMAIS) report, 2025 State of the States Overview. These states offer examples of the trending policy changes and investments governors intend to make, providing valuable insights into the evolving healthcare landscape.
Key Trends in Governors’ Budgets
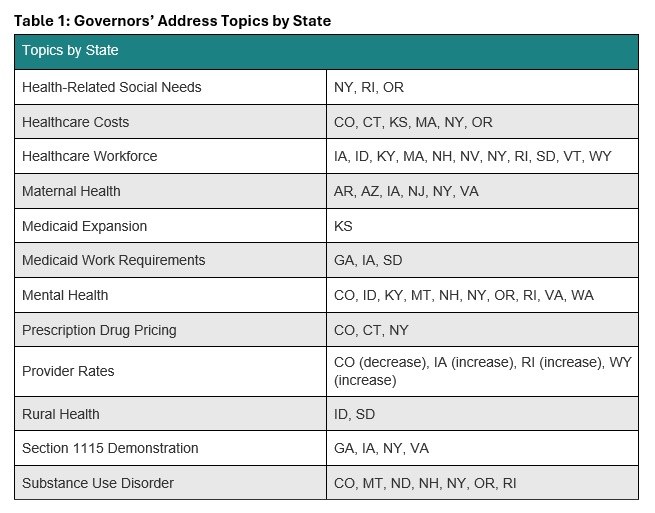
State of the State addresses provide insights into governors’ priorities, reflecting state budgets, multiyear initiatives, and changes in federal policies and funding. These priorities signal strategic shifts healthcare stakeholders must navigate to remain aligned with the evolving state and federal policy landscapes. Common themes that Health Management Associates (HMA) is tracking this year include healthcare affordability, Medicaid work requirements, workforce shortages, and enhanced oversight of healthcare entities.
Highlights by State
Illinois Gov. J.B. Pritzker delivered a 2025 State of the State Address on February 19, 2025, during which he presented his executive budget proposal for fiscal year (FY) 2026 and discussed strengthening oversight of healthcare entities like pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) and health insurers. Governor Pritzker introduced the Prescription Drug Affordability Act, which seeks to further regulate PBMs, reduce drug costs, and protect independent pharmacists. More specifically, it would give the state Department of Insurance full statutory authority to examine PBM records and require these organizations to comply with annual auditing and reporting requirements. The governor also called for a ban on prior authorization for behavioral healthcare and proposed requiring insurance companies to reimburse patients for reasonable travel costs for medical appointments when the distance they must travel exceeds network adequacy requirements.
Pritzker’s budget allocations include:
- $191.8 million to support the Certified Community Behavioral Health Clinic (CCBHC) Medicaid Demonstration Program
- $27.9 million to maintain the state’s maternal and child home health programs
- $27.7 million to support nonhospital facilities that provide psychiatric care to people younger than 21 years old
- $132 million for Medicaid-like coverage for undocumented adults ages 65 and older
- A shift in funding from the state’s Exchange to a State-Based Marketplace, which would end use of the federal platform
In addition, the budget plan eliminates funding for Medicaid-like coverage for undocumented adults ages 42−64, which cost approximately $420 million in one year.
Indiana Gov. Mike Braun delivered his address on January 29, 2025, during which he discussed his support for state legislation that would address healthcare costs. Governor Braun urged the legislature to pass multiple bills, including:
- House Bill (HB) 1003: Specifies that the state’s Medicaid Fraud Control Unit (MCFU) may investigate provider fraud, insurer fraud, and duplicate billing and would require more healthcare price transparency, stop anticompetitive practices that drive up prices, and put an end to surprise billing
- Senate Bill (SB) 3: Would mandate that third party administrators, PBMs, employee benefit consultants, and insurance providers acting on behalf of plan sponsors have a fiduciary duty to the plan sponsors
- HB 1004: Would bolster oversight of nonprofit hospital financials
The governor also encouraged the legislature to support efforts focused on PBM reforms.
Governor Braun’s proposed budget for the 2025−27 biennium recommends a general fund appropriation of more than $5 billion in FY 2025−26 and $5.3 billion in FY 2026−27 for the state Office of Medicaid Policy and Planning. Moreover, the state is still managing the effects of a nearly $1 billion shortfall it identified in the Medicaid budget in FY 2024. The Indiana Family and Social Services Administration predicts total Medicaid expenditures will reach nearly $21 billion in FY 2025, up 6.4 percent from $19 billion in 2024 and will likely increase by at least another $1 billion in both 2026 and 2027.
New Mexico Gov. Michelle Lujan Grisham delivered her 2025 State of the State Address on January 21, 2025, wherein she discussed the new state Health Care Authority (HCA), which launched in July 2024. According to Governor Grisham, the HCA has helped the state to increase Medicaid provider rates, create a Health Care Affordability Fund, and expand the Health Care Professional Loan Repayment Program. To continue with HCA’s work, the governor announced that in March 2025, the state will be sending more than $1 billion to New Mexico hospitals through the Medicaid provider tax. She also recommended that the state legislature approve $50 million in additional funding for the Rural Health Care Delivery Fund, which supports getting new and expanded primary, behavioral, maternal and child, and specialty healthcare services into rural areas.
In her proposed FY 2026 budget, the governor recommends:
- $13 million in recurring funds to increase reimbursement rates up to 150 percent of Medicare rates
- $5.3 million for the Program of All-Inclusive Care for the Elderly (PACE)
- $2.5 million for increased assisted living facility rates
- $2.9 million to increase behavioral health rates for non-Medicare equivalents
- $30 million annually over three years to expand Medicaid services, including medical respite for people who are homeless, food support for certain individuals who pregnant, infrastructure to provide medical services to people who are justice-involved, and infrastructure to provide housing and food supports.
In addition, the budget recommends a $100 million special appropriation to address behavioral health needs, which will fund the 988 program, an investment to secure a federal match for the CCBHC Initiative, more drug and alcohol treatment services at the New Mexico Behavioral Health Institute, and medical and behavioral health providers at the Corrections Department.
South Carolina Gov. Henry McMaster delivered his 2025 State of the State Address on January 29, 2025, in which he discussed the state’s siloed health and human services delivery system, which he said creates a difficult landscape to navigate for people with physical disabilities, special needs, and mental health issues. Governor McMaster said the state must make immediate changes to the Department of Mental Health and Department of Disabilities and Special Needs and proposed making the boards of commissioners that run the departments directly accountable to the governor.
The governor’s proposed FY 2025−26 budget highlighted his priority of reimplementing Medicaid work requirements through a Section 1115 demonstration waiver, which the state previously had in place during President Donald Trump’s first administration. Governor McMaster has already requested an expedited approval of the demonstration, which would expand Medicaid eligibility to 100 percent of the federal poverty level (FPL) for parents who are working or going to school. Under South Carolina’s existing eligibility rules, parents no longer qualify for Medicaid if they earn more than 67 percent of the FPL. The work and school requirements would only apply to parents with incomes of between 67 percent and 100 percent of the FPL.
The budget also recommends approximately $79 million in recurring funds to support the state’s Medicaid program. Those funds would be allocated as follows:
- $5.7 million toward increasing behavioral health provider payment rates
- $5.4 million toward increasing opioid use disorder provider reimbursement rates
- $10 million toward reducing waiting lists for home and community-based services
- $2.4 million toward intensive partial hospitalization and outpatient behavioral health programs
In addition, the budget recommends funding for the Department of Public Health and $1.6 million in nonrecurring funds and $625,000 in recurring funds for the Healthy Moms, Healthy Babies program and its mobile maternity care vehicle.
Connect With Us
HMAIS has prepared a comprehensive report summarizing each State of the State address and governors’ proposed budgets, which is available to HMAIS subscribers. It also comprises a section highlighting trends in the issues covered in each speech, including maternal health, substance use disorder, Medicaid work requirements, prescription drug prices, and provider rates.
HMA supports healthcare stakeholders in responding to these developments, offering strategic guidance and expertise to help navigate the evolving policy landscape and align with the shifting priorities outlined in these addresses. Contact one of our experts below for more information about the report or to connect with one of HMA’s state policy and market experts.