While the current federal COVID-19 Public Health Emergency (PHE) declaration could be in place through the winter months, HMA’s team of experts see many reasons to put the PHE’s Medicaid unwinding planning at the top of your list now.
Without an extension, the PHE declaration will expire on January 11, 2023. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) officials pledged to provide 60-days’ notice before ending the PHE. As a result, since HHS did not announce an extension by November 12, we can assume that HHS Secretary Xavier Becerra will extend the PHE beyond January.
However, congressional leaders are again considering proposals that would impact the PHE’s Medicaid policies. Such a change could advance during the lame duck session of Congress. For a variety of reasons, lawmakers could seek a statutory change that would de-link Medicaid’s continuous enrollment requirement, the 6.2 percentage point increase in the federal Medicaid match, and other Medicaid maintenance of effort policies from the PHE declaration. Congress could set a specific date for ending these Medicaid policies. Doing so would provide more certainty for planning for the end of the continuous Medicaid enrollment policy and its downstream implications for health insurance programs.
What can Medicaid agencies, health plans, providers and other stakeholders do now?
The transition from Medicaid’s continuous enrollment requirement to normal eligibility operations involves a myriad of policy decisions and operational changes that will impact enrollees. In turn, the end of Medicaid’s continuous coverage policy will also have great bearing on the business and operational strategies of managed care plans, providers and other stakeholders participating in the Medicaid and Marketplace programs.
HMA’s experts are working with state agencies, health plans, hospitals and health systems, and other stakeholders to identify options and workable solutions to prepare for these major changes. This work touches policy, organizational workstreams, systems, and payment. There are issues specific to Medicaid as well as the intersection with Marketplace, the Supplemental Nutrition Program (SNAP), and other public programs.
Combining our collective on-the-ground experience in states with our federal policy insights, experts from across the HMA family of companies list below themes and immediate actions stakeholders can consider. These action steps are focused on ensuring states, managed care plans, providers and other stakeholders are prepared to immediately respond to the end of the Medicaid continuous enrollment policy and work with individuals to provide information and other support they may need to stay enrolled in a coverage program.
1. Monitor and prepare for federal activities, particularly during the lame duck session of Congress and into 2023. Healthcare policies are likely to feature prominently in Congress’ lame duck session in November and December. Decoupling the Medicaid continuous enrollment and enhanced Federal Medical Assistance Percentage (FMAP) policies from the PHE is one issue under consideration. Any statutory changes to these policies may also include new requirements for the unwinding process. Stakeholders will want to closely monitor these discussions.
If Congress sets a statutory end date for the PHE’s Medicaid eligibility policies, this will provide the certainty needed for states to finalize PHE unwinding action plans with target dates for resuming normal eligibility operations. Notably, this may also drive conversations during states’ 2023 legislative sessions.
Consider the impact to your state and your organization – and any decisions you’ll be faced with – if the enhanced FMAP is decoupled from the PHE. For example, if your state had the option to maintain continuous eligibility without the enhanced FMAP, would it do so? States and stakeholders will want to revisit their Medicaid unwinding plans, consider options for meeting any new requirements, and update existing plans accordingly. Also, stakeholders can offer to serve as a resource to your state Medicaid agency and/or Congressional delegation regarding lame duck legislative proposals pertaining to Medicaid and the PHE.
2. Stay informed about state-specific landscapes. With statewide elections largely decided and expectations for a PHE end date sometime in the first part of 2023, now is the time for stakeholders to revisit when and how to engage with state Medicaid and other state agencies to support Medicaid eligibility unwinding plans. Stakeholders will want to solidify strategies and timing for engaging with states as unwinding plans are further solidified and eventually implemented.
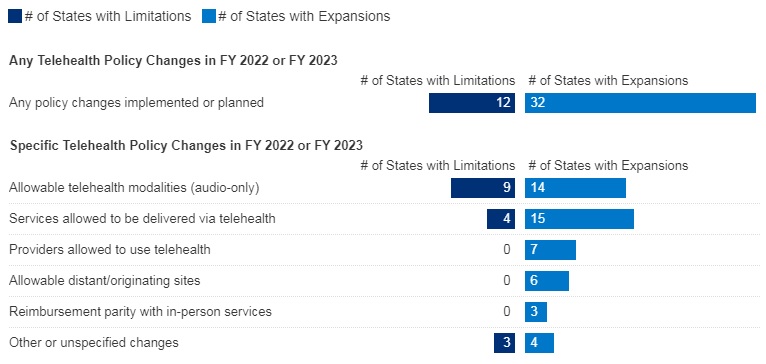
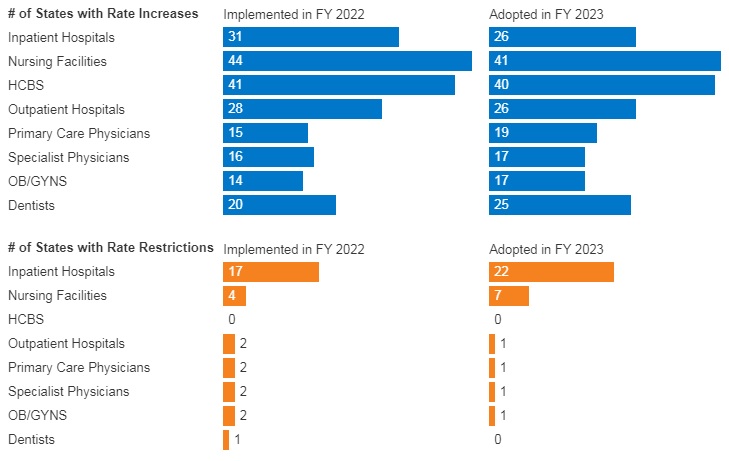
Stakeholders can also monitor changes to states’ eligibility and enrollment rules – including initiatives designed to simplify eligibility rules, enhance eligibility and enrollment systems, and adjust managed care rate setting policies, among others. Many states are utilizing the temporary federal Medicaid flexibilities to alleviate the significant eligibility unwinding workload. Federal agencies also continue to regularly publish new information for states and stakeholders to consider. Some states are implementing policies designed to improve the transition from Medicaid to Marketplace. Understanding the implications of such policies will help stakeholders anticipate how ending Medicaid’s continuous coverage requirement will directly affect them.
3. Refresh strategies and messaging for outreach and assistance. While the PHE end date remains in flux, state plans for ending the Medicaid continuous coverage policy are still evolving. States are refining their beneficiary communication plans and may be developing updated guidance for stakeholders. Health plans, providers, and other stakeholders should align their messaging and outreach work accordingly and continue to build partnerships in communities across the state.
However, outreach alone will not be enough to reach all Medicaid enrollees. Many will need assistance in understanding and complying with changes that come with the end of the continuous enrollment policy. For example, stakeholder-provided redetermination assistance will be key to minimizing the number of enrollees who lose coverage for failure to complete the redetermination process and state requirements for stakeholder assistance will vary state by state.
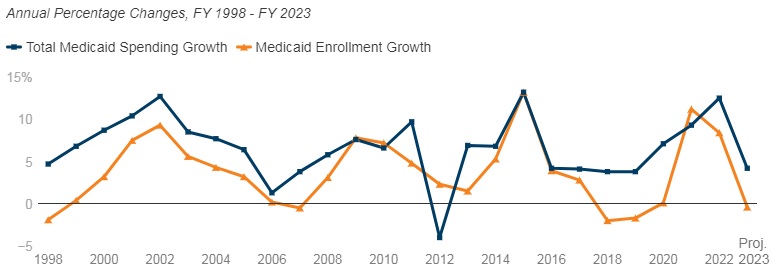
4. Update projected impact of enrollee transitions between Medicaid and Marketplace programs. For states and stakeholders, especially health plans, it is time to update projections about 2023 Medicaid and Marketplace enrollment. This may also require new analysis and strategies to address the changing population acuity and resulting impact on capitation revenue. For healthcare providers, health systems, and other healthcare facilities, the end of the Medicaid continuous enrollment policy is expected to drive significant changes in payer mix, and it could reduce revenue as well as impact qualifications for special payment programs, the 340B program, among others. Understanding these dynamics can help with budgeting and implementation of specific patient outreach and support strategies.
5. Develop strategies to translate experiences from Medicaid to Marketplace. Medicaid agencies, managed care plans, and providers have gained valuable insights about the needs of individuals who have remained continuously enrolled in Medicaid during the COVID-19 PHE. This is particularly true for Medicaid enrollees diagnosed with a mental illness, substance use disorder, or both. Medicaid providers and health plans have gained valuable insight on effective clinical care models, whole person care, partnerships with community-based organizations and reimbursement strategies that can better meet the needs of complex populations. Providers and plans can utilize these experiences to better support the millions of individuals who are expected to become eligible for Marketplace coverage after Medicaid’s continuous enrollment policy ends.
The HMA team continues to monitor the dynamic state and federal policy landscapes, including state planning documents and new federal guidance and informational tools. We have the ability to support stakeholders to prepare for the end of PHE and to support state and communities by modeling projected enrollment and payer mix changes across health coverage categories. Stakeholders should be using this time to address gaps in their plans for PHE unwinding and continue to identify and evaluate new options that may emerge to support beneficiaries in retaining health coverage.
This blog was written by Jane Longo, Andrea Maresca and Bill Snyder.
 In December 2021, CMS approved
In December 2021, CMS approved  New York, like North Carolina, plans to seek CMS’ approval to offer a range of community services that would be provided through newly established networks of community-based organizations in all regions of the state. The state envisions that the CBO networks will include small neighborhood organizations familiar with their communities’ needs and the capacity to address multiple social risk factors as well as larger county or regionally focused entities. In addition, New York is asking CMS to support a health equity focused proposal which would provide certain “in-reach” services for incarcerated individuals before they are released.
New York, like North Carolina, plans to seek CMS’ approval to offer a range of community services that would be provided through newly established networks of community-based organizations in all regions of the state. The state envisions that the CBO networks will include small neighborhood organizations familiar with their communities’ needs and the capacity to address multiple social risk factors as well as larger county or regionally focused entities. In addition, New York is asking CMS to support a health equity focused proposal which would provide certain “in-reach” services for incarcerated individuals before they are released. Oregon submitted a request to use federal Medicaid spending authority to address community-based health inequities and to establish statewide health equity investments (HEIs). The state is especially focused on supporting consumers during disruptions in coverage, life transitions, or disruptions caused by climate events. Community-based investments will reflect empirical evidence and community assessments and may include efforts to improve building environments and expand culturally and linguistically. Addressing climate events may be of particular interest as it addresses multiple priorities for Administration.
Oregon submitted a request to use federal Medicaid spending authority to address community-based health inequities and to establish statewide health equity investments (HEIs). The state is especially focused on supporting consumers during disruptions in coverage, life transitions, or disruptions caused by climate events. Community-based investments will reflect empirical evidence and community assessments and may include efforts to improve building environments and expand culturally and linguistically. Addressing climate events may be of particular interest as it addresses multiple priorities for Administration.